In Fig. 1 the whole experimental apparatus for measuring electrons
ejected at zero-degrees to the beam direction in ion-atom collisions
is shown.
The chamber
consists of two cylindrical parts. The lower chamber is pumped by
a 450 l/s turbomolecular pump and supports the hemisperical spectrograph.
The upper chamber is removable for easy
accessibility and manipulation of components inside the chamber. Both lower
and upper part have an inner cylinder made of ![]() -metal used to reduce the
earth's magnetic field to a few mGauss.
Viton O-rings are used in all chamber joints. A base pressure of
-metal used to reduce the
earth's magnetic field to a few mGauss.
Viton O-rings are used in all chamber joints. A base pressure of ![]() Torr
was attained.
Torr
was attained.
The target consists of a doubly differentially pumped
gas-cell mounted in a 4 ![]() 5-way cross in front of the
chamber and pumped by a second 170 l/s turbomolecular pump.
The gas pressure is measured by a baratron manometer. The gas-cell is 50 mm
long and has removable entrance and exit apertures. Typical aperture sizes
were 3mm. Two cylindrical baffles were placed on
either side of the gas-cell to further improve the differential pumping.
Thus, a pressure ratio (pressure
inside gas-cell/pressure inside chamber) of more than 10,000 for the case of
He was established.
5-way cross in front of the
chamber and pumped by a second 170 l/s turbomolecular pump.
The gas pressure is measured by a baratron manometer. The gas-cell is 50 mm
long and has removable entrance and exit apertures. Typical aperture sizes
were 3mm. Two cylindrical baffles were placed on
either side of the gas-cell to further improve the differential pumping.
Thus, a pressure ratio (pressure
inside gas-cell/pressure inside chamber) of more than 10,000 for the case of
He was established.
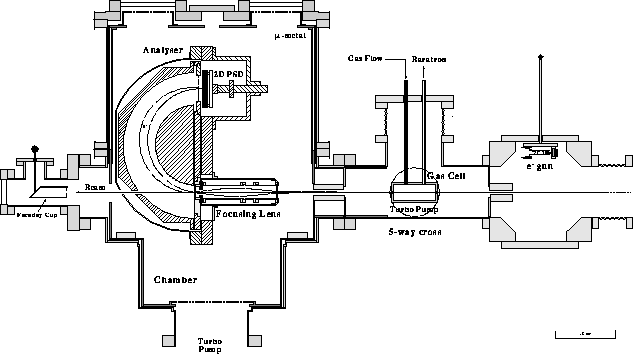
Figure: The zero-degree experimental setup.